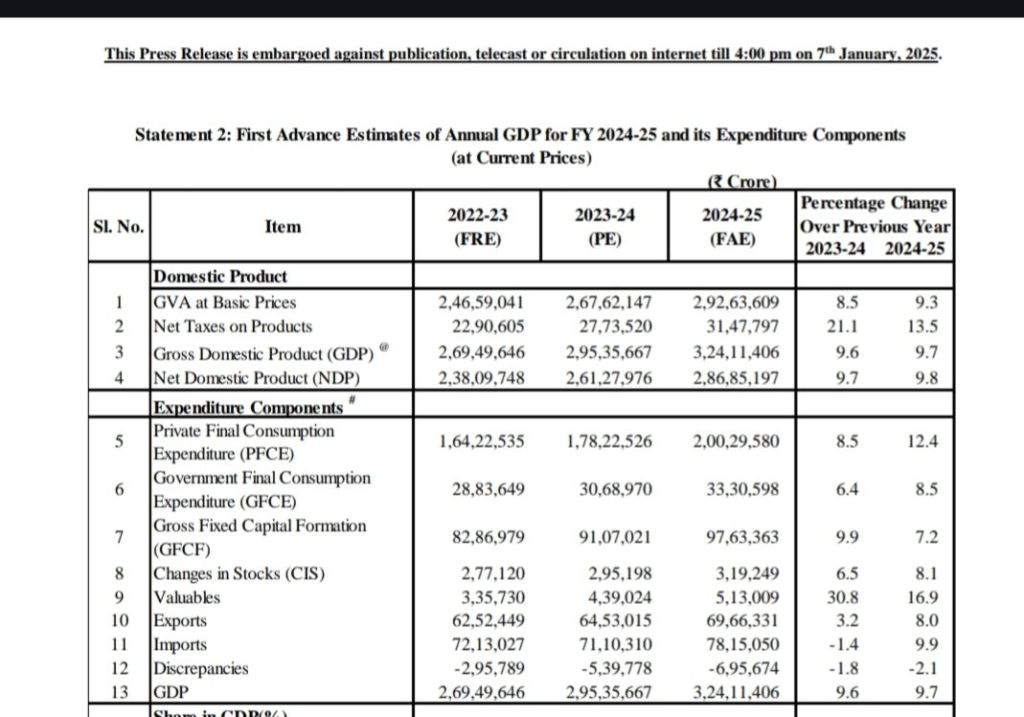
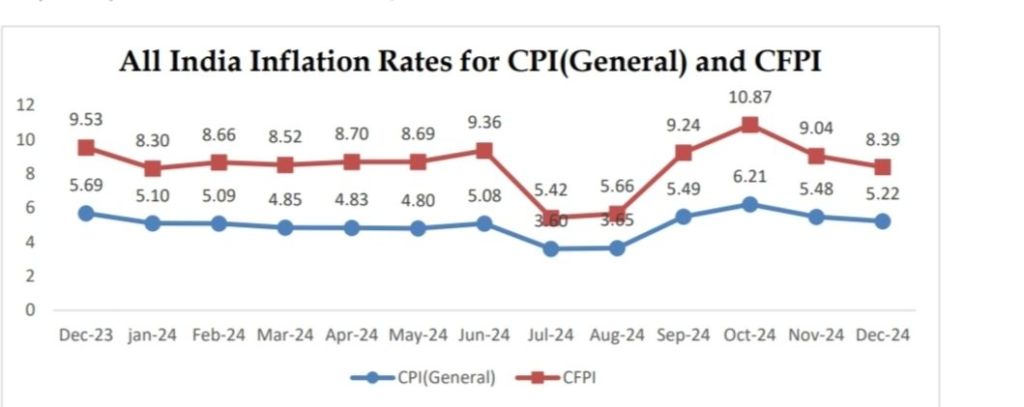
India’s economic trajectory in FY 2024-25 presents a tale of resilience and challenges. The nation is set to achieve an impressive nominal GDP growth of 9.7%, supported by strong private consumption (12.4%) and steady government expenditure (8.5%). However, this robust growth narrative is tempered by persistent food inflation, which averaged 8.31% from April to December 2024. While general inflation (CPI) remained moderate at 4.93%, the high food prices threaten to erode real income gains, particularly for vulnerable households.
The challenge for policymakers is clear: to sustain economic momentum while addressing inflationary pressures. Both the upcoming Union Budget 2025-26 and the collaborative efforts of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and the Ministry of Finance will play a pivotal role in striking this balance.
Economic Growth vs. Inflation: A Delicate Trade-off
Economic Growth: Strength in Numbers
India’s nominal GDP growth of 9.7% is a testament to its economic resilience. Key drivers include rising private consumption, investments, and a recovering global environment. Increased spending on infrastructure and rural development has bolstered demand, creating a multiplier effect across sectors.
However, the benefits of this growth are not equally distributed. High food inflation, which consistently outpaced general inflation, disproportionately affects low-income and rural households, where food constitutes a significant share of consumption. Rural food inflation, averaging higher than urban rates, highlights the uneven economic recovery.
Inflation: Persistent Pressures
While general inflation (CPI) has moderated, food inflation at 8.31% remains a significant concern. October 2024 saw food inflation peak at 10.87%, before declining to 8.39% in December. This persistent pressure on food prices—due to supply chain inefficiencies, rising input costs, and climatic uncertainties—continues to erode purchasing power, threatening to derail household budgets.
The Union Budget 2025-26: A Balancing Act
The Union Budget offers an opportunity to align fiscal policy with the dual objectives of fostering growth and curbing inflation. Key measures that could be undertaken include:
1. Agricultural Reforms and Food Supply Chains
- Investment in irrigation, crop diversification, and modern agricultural technology can stabilize food production.
- Strengthening cold storage and logistics infrastructure can reduce post-harvest losses and ensure price stability for essential commodities.
2. Subsidies and Welfare Schemes
- Targeted subsidies for essential commodities and agricultural inputs will provide relief to farmers and rural households.
- Expanding direct benefit transfers (DBT) can cushion low-income groups from food price shocks without distorting market dynamics.
3. Tax Reforms
- Rationalizing GST rates on essential food items and agricultural inputs will help curb retail inflation.
- Tax incentives for agritech startups and the food processing industry can encourage innovation and efficiency in the food supply chain.
4. Promoting Consumption
- Increased allocations for employment schemes like MGNREGA will provide liquidity to rural households, stimulating consumption.
- Urban-focused measures, such as affordable housing initiatives and middle-class tax reliefs, will boost overall demand.
The Role of the Reserve Bank of India
The RBI’s role in managing inflation while supporting growth is pivotal. It must strike a delicate balance through its monetary policy:
- Inflation Management:
- While general inflation remains within target, persistent food inflation necessitates vigilance. The RBI may continue using repo rate adjustments to manage liquidity and inflation expectations.
- Credit Growth:
- The central bank should ensure that sectors like agriculture, MSMEs, and infrastructure receive adequate and affordable financing to drive growth.
- Global Monitoring:
- External factors, including global commodity prices and supply chain disruptions, could influence domestic inflation. The RBI must proactively align its policies to address these risks.
The Ministry of Finance: Fiscal Responsibility and Growth

The Ministry of Finance must adopt a balanced approach to sustain economic growth while maintaining fiscal discipline:
- Managing Fiscal Deficit:
- Increased public expenditure must be matched with credible fiscal deficit targets to enhance investor confidence and macroeconomic stability.
- Boosting Investments:
- By focusing on capital expenditure for infrastructure and logistics, the government can address supply-side bottlenecks and reduce inflationary pressures.
- Coordination with the RBI:
- Close synergy between monetary and fiscal policies will ensure a unified approach to tackling inflation and supporting growth.
Opportunities and Risks
India’s economic growth story is compelling, but the persistent challenge of inflation—especially food inflation—poses significant risks. The narrowing gap between nominal GDP growth (9.7%) and food inflation (8.31%) underscores the need for inclusive economic policies that prioritize both growth and price stability.
Opportunities:
- Strong nominal GDP growth provides fiscal headroom for targeted spending and investment.
- Controlled general inflation creates a stable environment for investment and consumption.
Risks:
- Persistent food inflation threatens to erode household purchasing power, particularly in rural areas.
- Global uncertainties, such as fluctuating commodity prices, could exacerbate inflationary pressures.
Conclusion: A Path Forward
India stands at a critical juncture where bold and balanced policy decisions can ensure sustainable and inclusive growth. The Union Budget 2025-26 must prioritize agricultural reforms, infrastructure investments, and targeted welfare measures to tackle food inflation and boost rural and urban consumption. Simultaneously, the RBI must maintain a vigilant yet accommodative stance to manage inflation without stifling growth.
By addressing both immediate inflationary concerns and long-term structural challenges, India can create a virtuous cycle of growth, stability, and equity. Only by fostering a collaborative effort between the government, the central bank, and industry stakeholders can the nation fully realize its economic potential and ensure that its growth story benefits every citizen.